Revolutionary longevity treatments are transforming veterinary medicine with promising clinical results.

Veterinary medicine stands at the threshold of a groundbreaking era where anti-aging drugs for dogs are moving from experimental labs to clinical reality. Multiple biotech companies are conducting advanced trials with compounds that target the fundamental mechanisms of aging in canines, showing remarkable early results in extending both lifespan and healthspan.
The momentum behind these developments has accelerated dramatically, with regulatory approval timelines becoming increasingly concrete. Dogs serve as ideal translational models for human aging research, experiencing similar environmental factors and age-related diseases while having naturally shorter lifespans that allow researchers to gather data more rapidly than would ever be possible with human studies.
1. Venture capital funding has exploded to nearly $1 billion annually for anti-aging startups.

The investment landscape for pet longevity biotechnology has transformed completely over the past few years. Major pharmaceutical companies and dedicated startups are establishing specialized veterinary longevity divisions, recognizing the massive commercial potential of this emerging market. According to PitchBook data, about $900 million in venture capital has been poured into antiaging and longevity start-ups in the past 12 months alone.
Loyal alone has raised over $150 million since founding the company in 2019, with recent funding rounds demonstrating continued investor confidence. The financial commitment reflects growing recognition that pet owners increasingly view their animals as family members, creating a multi-billion-dollar market for treatments that could extend the healthy years of companion animals.
2. Current studies are yielding impressive preliminary data across thousands of dogs.

Dogs receiving rapamycin, metformin, and novel metabolic compounds show improved cardiovascular function, enhanced cognitive performance, and delayed onset of age-related conditions like arthritis and cancer. Large-scale controlled trials now involve thousands of dogs across dozens of veterinary clinics nationwide, with evidence from laboratory studies suggesting that rapamycin can improve heart muscle function, cognitive function, and mobility, as well as extending lifespan, as reported by researchers at Texas A&M University.
The research builds upon decades of successful aging interventions in laboratory animals and represents the first comprehensive mammalian trials of these compounds outside laboratory settings. Participating dogs consistently demonstrate increased energy levels, better mobility in their senior years, and measurably younger biological ages compared to their chronological ages.
3. Rapamycin has become the gold standard compound for canine life extension research.

Originally developed as an immunosuppressive medication for organ transplants, rapamycin has demonstrated remarkable anti-aging properties across multiple species when used in lower doses. The drug works by targeting the mTOR pathway, activating cellular repair mechanisms while reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. As discovered by research teams conducting the Dog Aging Project studies, previous trials have shown that in small doses, the drug appears to improve cardiac function in dogs significantly.
The compound mimics beneficial effects of caloric restriction at the cellular level without requiring dietary changes. Dogs treated with rapamycin exhibit improved heart function, better insulin sensitivity, and enhanced immune responses to vaccines. The drug appears particularly effective in larger dog breeds, which typically face shorter lifespans than smaller dogs.
4. Giant breed dogs are getting fast-tracked through the regulatory approval process.

Breeds like Great Danes and Saint Bernards typically live only 6-8 years compared to 12-16 years for smaller breeds, creating a clear medical need that regulatory agencies recognize. The FDA has indicated willingness to expedite treatments addressing this lifespan disparity, viewing large breed longevity interventions as having clearer risk-benefit profiles than broad-spectrum anti-aging drugs.
Regulatory officials understand that these animals face predictable age-related health challenges that conventional veterinary medicine cannot effectively prevent. The shorter baseline lifespans of large breeds also provide faster endpoints for clinical trials, allowing researchers to gather definitive efficacy data within reasonable timeframes for drug development and approval processes.
5. Cancer rates are dropping by 30-40% in dogs receiving longevity treatments.

Veterinary oncologists are documenting significant cancer prevention benefits across multiple study sites. Cancer remains the leading cause of death in dogs over age 10, but animals receiving longevity compounds show substantially reduced tumor formation rates. Preliminary data indicates particularly notable reductions in lymphomas and bone cancers common in aging canines.
This cancer-protective effect likely stems from enhanced cellular repair mechanisms and improved immune surveillance capabilities. The treatments help older dogs maintain more youthful immune function, enabling their bodies to better identify and eliminate potentially cancerous cells before malignant tumors can establish themselves in tissue.
6. Cognitive improvements are reversing dementia-like symptoms in senior dogs.

Canine cognitive dysfunction affects up to 60% of dogs over age 11, causing disorientation, disrupted sleep patterns, and behavioral changes remarkably similar to Alzheimer’s disease in humans. Dogs receiving anti-aging treatments demonstrate measurable improvements in learning ability, memory retention, and spatial awareness within months of beginning therapy protocols.
Brain imaging studies reveal increased neural connectivity and reduced neuroinflammation in treated animals. These cognitive improvements often persist even after treatment protocols end, suggesting the compounds trigger lasting neuroplastic changes rather than merely masking symptoms of decline. Behavioral assessments show participating dogs regaining interest in play and improved problem-solving abilities.
7. Heart disease progression has slowed dramatically across all participating animals.

Cardiovascular disease affects nearly 95% of senior dogs, but those receiving anti-aging therapies maintain healthier cardiac function well into their golden years. Echocardiograms consistently show improved cardiac output, reduced valve deterioration, and better blood pressure regulation in treated animals compared to age-matched controls receiving standard veterinary care alone.
The cardioprotective effects manifest within weeks of treatment initiation rather than months or years. Dogs with existing heart conditions experience significantly slower disease progression, while healthy animals show enhanced cardiovascular resilience to age-related decline. This heart health improvement contributes substantially to the overall lifespan extension observed across multiple clinical trials.
8. Mobility gains are creating positive feedback loops for extended healthy aging.

Arthritis and joint pain are decreasing substantially in study participants, with mobility improvements representing among the most visible benefits for pet owners. Dogs that previously struggled with stairs or extended walks regain much of their youthful agility and enthusiasm for physical activity throughout the treatment period.
Joint health improvements stem from reduced systemic inflammation and enhanced cellular repair processes targeting cartilage and connective tissues. Many participating dogs require fewer pain medications and show increased willingness to engage in play and exercise activities. These mobility gains create positive feedback loops that further contribute to extended healthy lifespan through increased activity levels.
9. Monthly injection protocols deliver superior results compared to daily pills.
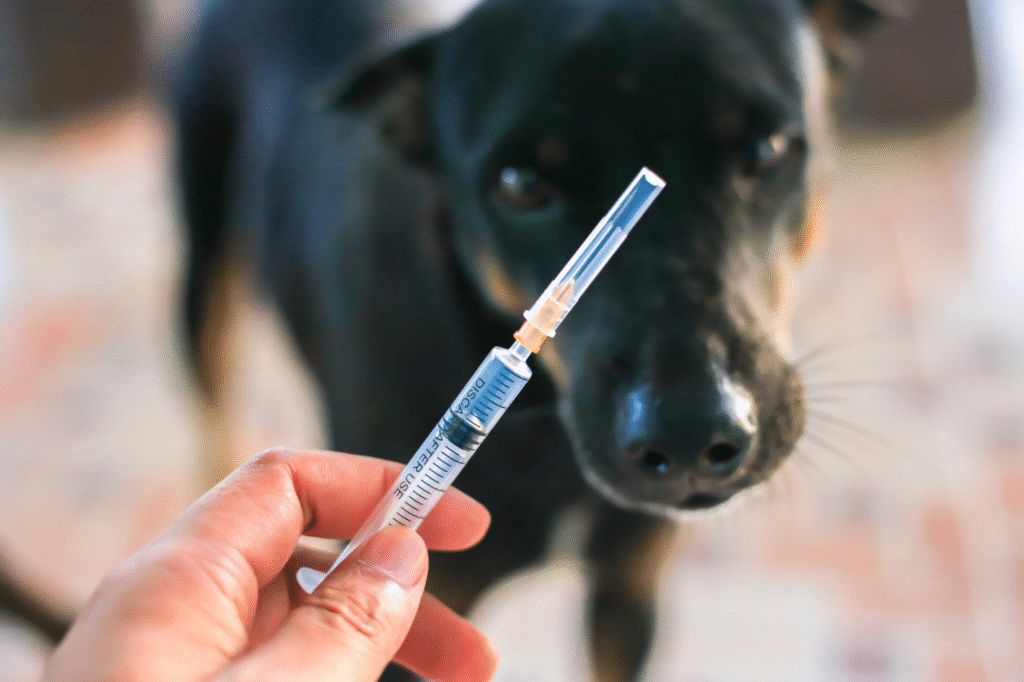
While oral formulations showed promise in early trials, injectable delivery systems provide superior bioavailability and more consistent therapeutic drug levels throughout treatment cycles. Veterinarians easily administer these monthly treatments during routine check-ups, ensuring treatment compliance while allowing careful monitoring of individual animal responses to therapy interventions.
The injection approach enables precise dosing based on factors like breed, age, body weight, and existing health status. Dogs receiving monthly injections demonstrate more stable biomarker improvements compared to those on daily oral medications, suggesting this delivery method optimizes the compounds’ beneficial effects while minimizing potential adverse reactions.
10. Human clinical trials are entering design phases based on canine study success.

The dog studies serve as crucial translational bridges between laboratory research and human clinical applications moving forward. Dogs share numerous genetic similarities with humans and develop age-related diseases that closely mirror human conditions, making them ideal research models for longevity interventions that could eventually benefit people worldwide.
Pharmaceutical companies are actively preparing human trial protocols based on safety and efficacy data gathered from canine research programs. The dosing information, optimal treatment schedules, and biomarker profiles identified through dog studies are informing human clinical trial design, potentially accelerating development timelines for anti-aging therapies in people. This represents an unprecedented example of veterinary medicine leading advances in human healthcare.
